Physical specifications of the RasPiGNSS “Betelgeuse” module
- Dimensions: 41 x 56mm (excluding SMA connector)
- Weight: 15g
- Antenna connector: SMA female
- Antenna power:
- Power supply: through Raspberry Pi expansion port (P1) or USB connector (configurable via solder jumper)
- Serial communications: through Raspberry Pi expansion port (P1), 2 independent UARTs
- I²C communications: through Raspberry Pi expansion port (P1) and pin header connector
- Status indication: through programmable LEDs and pin header connector
- For detailed electrical and environmental specifications see the ZED-F9P datasheet.
RasPiGNSS connectors
The RasPiGNSS “Betelgeuse” features a number of connectors and peripheral devices, which you can see in the image below. These are described in detail in the following sections.
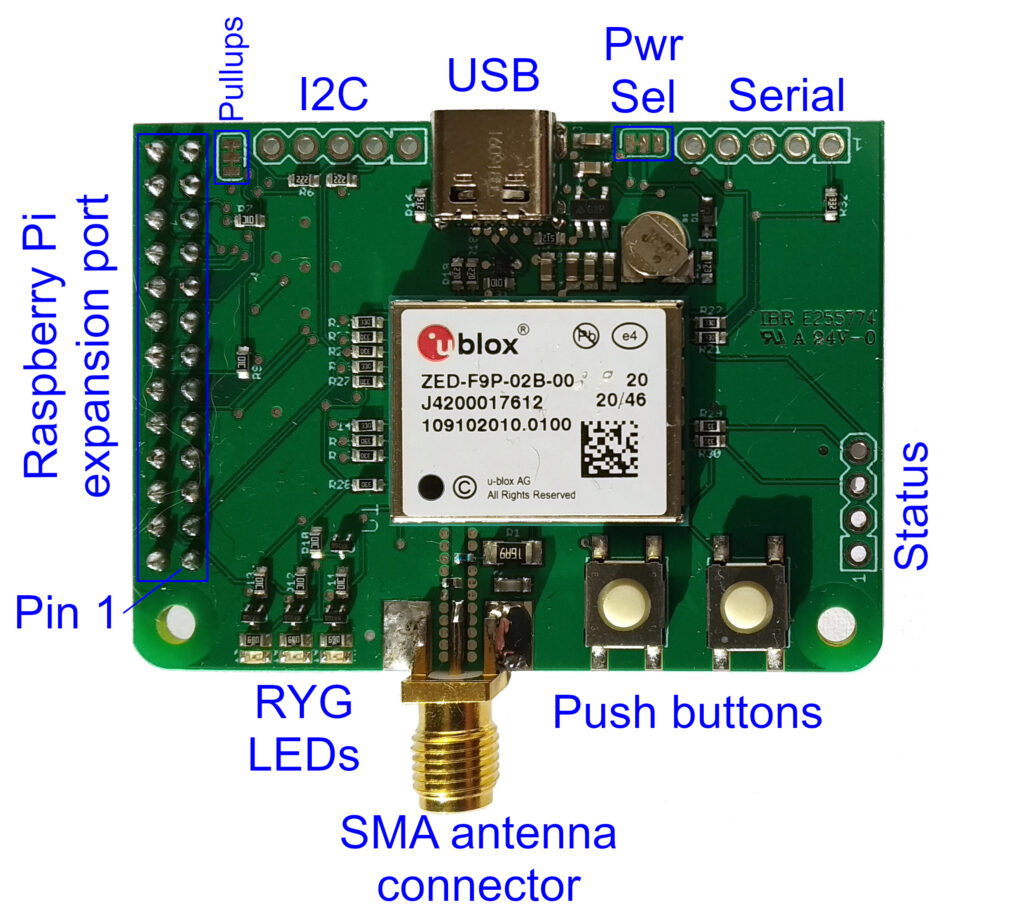
USB connector and power selection
The RasPiGNSS “Betelgeuse” board can either be operated as an add-on module (hardware-on-top, HAT) to the Raspberry Pi minicomputer (the default mode of operation), or as a standalone GNSS receiver using the USB-C connector of the board. In this case, power would also need to be drawn from the USB-C connector. To configure this mode of operation, the solder jumper located to the right of the USB connector in the image above (marked as “Pwr Sel”) needs to be reconfigured: Cut the trace from the middle pad to the left pad, and solder the middle pad to the right pad. This connection is not enabled by default, as the RasPiGNSS board might be damaged, if power is provided at the same time both from the Raspberry Pi and from the USB port, therefore this solder jumper needs to be reconfigured to the desired operation mode.
Note: Any improper hardware modification will void warranty of the RasPiGNSS board! Please contact us if you want to have this modification done prior to shipping the RasPiGNSS.
Note: In the default (unmodified) power selection jumper configuration you may connect a USB cable while the RasPiGNSS board is powered from the Raspberry Pi, e.g. for updating GNSS chip firmware over USB. This is possible since the RasPiGNSS doesn’t draw power from the USB port, yet USB communications will be enabled when plugging in a USB connector.
RasPiGNSS expansion port (P1) connections
| P1 Pin | GPIO | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1-1 | +3.3V | Power supply to the ZED-F9P | |
| P1-2 | +5V | Analog and digital power supply, not used by the ZED-F9P | |
| P1-4 | +5V | Analog and digital power supply, not used by the ZED-F9P | |
| P1-6 | GND | Ground | |
| P1-7 | GPIO4 | SW1 | Tactile switch 1 |
| P1-8 | GPIO14 | RX1 | Serial receive of the ZED-F9P, Raspberry Pi TXD0 signal |
| P1-10 | GPIO15 | TX1 | Serial transmit of the ZED-F9P, Raspberry Pi RXD0 signal |
| P1-11 | GPIO17 | SW2 | Tactile switch 2 |
| P1-12 | GPIO18 | RST | Reset line to the ZED-F9P (active low) |
| P1-13 | GPIO27 | TIMEPULSE | Time pulse output of the ZED-F9P |
| P1-15 | GPIO22 | LED1 | Red indicator LED |
| P1-16 | GPIO23 | LED2 | Yellow indicator LED |
| P1-18 | GPIO24 | LED3 | Green indicator LED |
| P1-19 | GPIO10 | EXTINT | Programmable external interrupt input to the ZED-F9P |
| P1-21 | GPIO9 | TXD2 | 2nd serial port transmit to the ZED-F9P |
| P1-22 | GPIO25 | TX_READY | Programmable transmit ready signal from the ZED-F9P |
| P1-24 | GPIO8 | RXD2 | 2nd serial port receive from the ZED-F9P |
| P1-26 | GPIO7 | SAFEBOOT_N | SAFEBOOT line to the ZED-F9P (active low) |
Note: LEDs or switches are not controlled by the NV08C, all I/Os are fully programmable from the RasPi.
All LEDs are standard 20mA types and are driven from the RasPi via a MOSFET.
Configure pins 15, 16, and 18 as outputs and set them high to switch them on.
All switches are directly wired to ground. Enable pullups on pins 7, and 11, and do debouncing in software to read them correctly.
I2C connector
The I2C connector provides access to the Raspberry Pi’s I2C-1 bus.
| I2C pin | P1 pin | GPIO | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2C1 | P1-5 | GPIO3 | SCL1 | I2C clock |
| I2C2 | P1-3 | GPIO2 | SDA1 | I2C data |
| I2C3 | P1-6 | – | GND | Ground |
| I2C4 | P1-1 | – | +3V3 | +3.3V power supply |
| I2C5 | P1-2, P1-4 | – | +5V | +5V power supply |
Note that all I2C signals (
SCL1,SDA1) have +3.3V logic levels. Connecting to a device with +5V logic levels may damage your Raspberry Pi! TheI2C5+5V pin is provided for convenience only, e.g. for devices providing an internal voltage regulator (as some Pololu IMUs do). There are two on-board pull-up resistors for SDA and SCL of the I2C bus, which can be activated by shortening a solder bridge.
ZED-F9P 2nd serial port connector
The SER connector provides access to the second serial port of the ZED-F9P GNSS chip on the RasPiGNSS “Aldebaran”. This port can be freely programmed e.g. for providing RTCM corrections to the ZED-F9P.
| SER pin | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SER1 | RXD2 | ZED-F9P port 2 serial receive |
| SER2 | TXD2 | ZED-F9P port 2 serial transmit |
| SER3 | GND | Ground |
| SER4 | +3V3 | +3.3V power supply |
| SER5 | +5V | +5V power supply |
Note that all SER signals have +3.3V logic levels. Connecting to a device with +5V logic levels may damage the GNSS chip of the RasPiGNSS! The
SER5+5V pin is provided for convenience only, e.g. for devices providing an internal voltage regulator.
Status connector
The RasPiGNSS “Betelgeuse” is equipped with a status port connector which features the following pinout:
| Status port pin | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | TIMEPULSE | Timepulse output of the ZED-F9P |
| 3 | GEOFENCE_STAT | Geofence status output of the ZED-F9P |
| 4 | RTK_STAT | RTK solution status output of the ZED-F9P |
Note: All signals of the status connector use +3.3V logic levels. Using voltage levels above +3.3V may permanently damage the RasPiGNSS board!
| ⯅ RasPiGNSS "Betelgeuse" |


